On-page SEO Process
In the ever-evolving world of digital marketing, mastering On-page SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is crucial for anyone looking to boost their website’s visibility and rankings on search engines. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you through the on-page SEO process step by step, ensuring that your website is optimized to its fullest potential.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO is all about fine-tuning specific web pages to boost their search engine rankings and draw in more natural, organic traffic. It involves various techniques and strategies that are implemented directly on your website to make it more search engine-friendly.
URL Structure:
Keep it Simple: Create clear, concise, and easy-to-understand URLs that convey the page’s topic.
Use Keywords: Include relevant keywords in your URLs to give both users and search engines a clear idea of your page’s content.
Short and Sweet: Aim for shorter URLs whenever possible, as they tend to be more user-friendly and easier to remember.
Structure Hierarchy: Organize your URLs hierarchically to reflect your website’s content structure. For example: domain.com/category/subcategory/page.
Canonicalization: Implement canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a URL, especially for duplicate content.
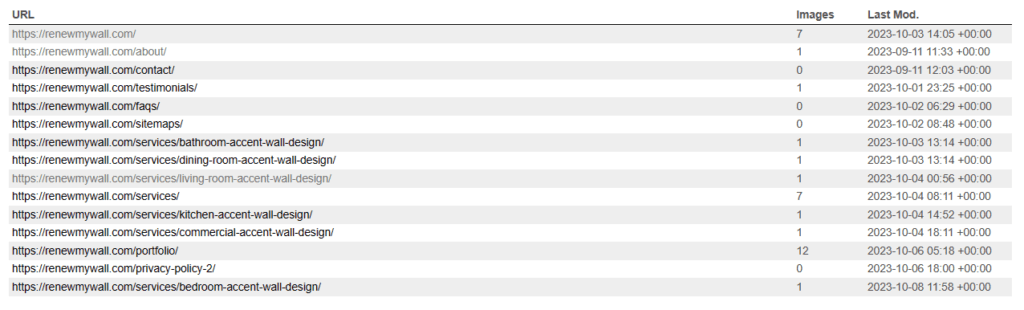
Title Tag:
Page Relevance: Craft title tags that accurately reflect the content of your web page, helping both users and search engines understand its purpose.
Keyword Placement: Include your primary keyword near the beginning of the title tag, but keep it natural and compelling to entice clicks.
Unique Titles: Ensure that each page on your website has a unique title tag to avoid confusion and improve search engine indexing.
Optimal Length: Aim for title tags between 50-60 characters to display well in search results without being cut off.
Branding: Incorporate your brand name if relevant, typically at the end of the title tag, to enhance recognition.
Front-Load Important Information: Place the most crucial information near the start of the title tag to capture immediate attention.
Consistency: Maintain a consistent format for title tags across your website, making it easier for both users and search engines to navigate.
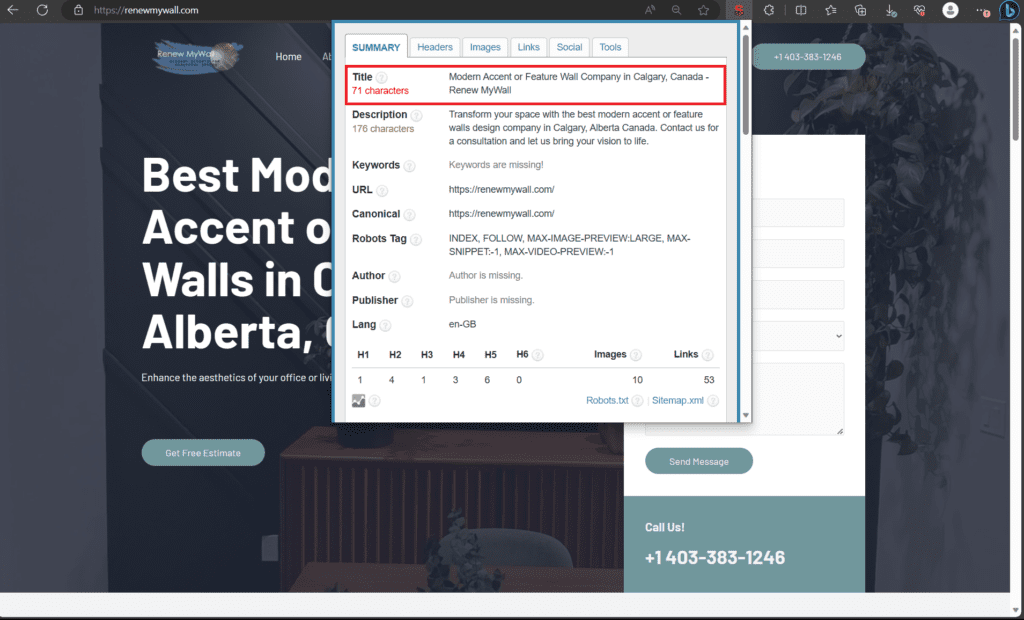
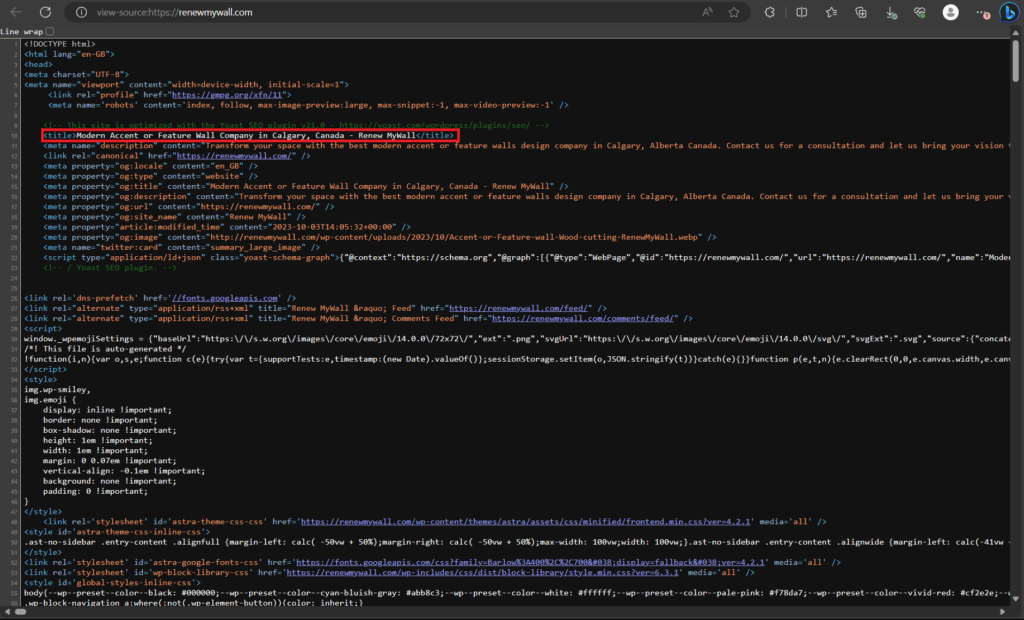
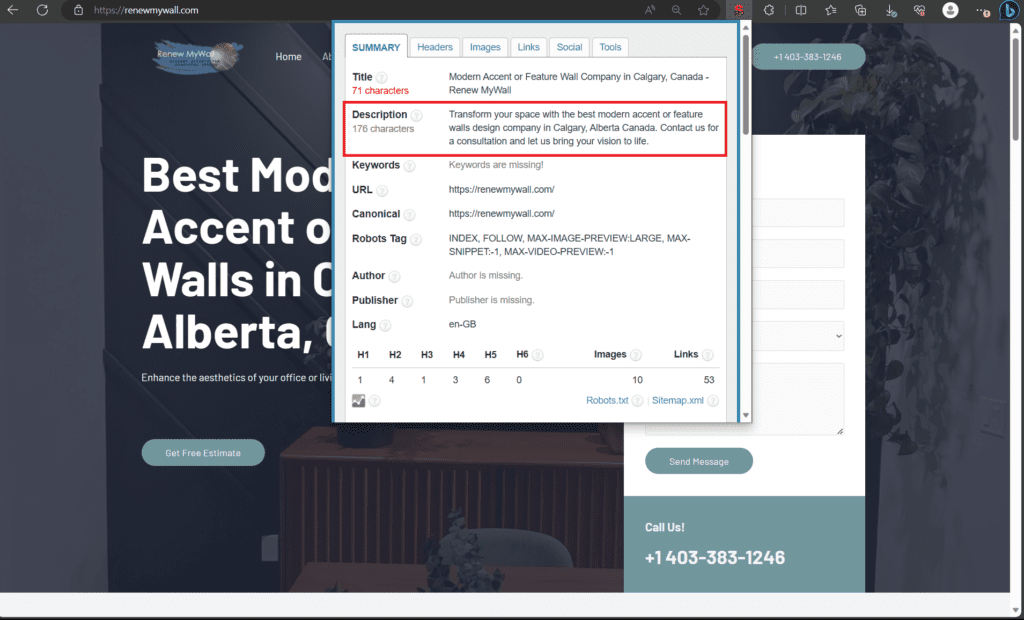
Meta Description:
Concise Summaries: Craft meta descriptions as concise summaries of your web page’s content, offering a glimpse of what users can expect.
Unique Descriptions: Ensure that each page has a unique meta description to avoid duplication and provide accurate information.
Include Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords naturally into the meta description to improve search engine visibility.
Optimal Length: Aim for meta descriptions between 150-160 characters to provide enough information without being cut off in search results.
Address User Needs: Highlight how your page addresses the specific needs or questions that users might have.
Call to Action (CTA): Consider including a clear and relevant call to action, encouraging users to take a desired action on your website.
Avoid Duplicate Content: Steer clear of using the same meta description across multiple pages, as this can confuse search engines.
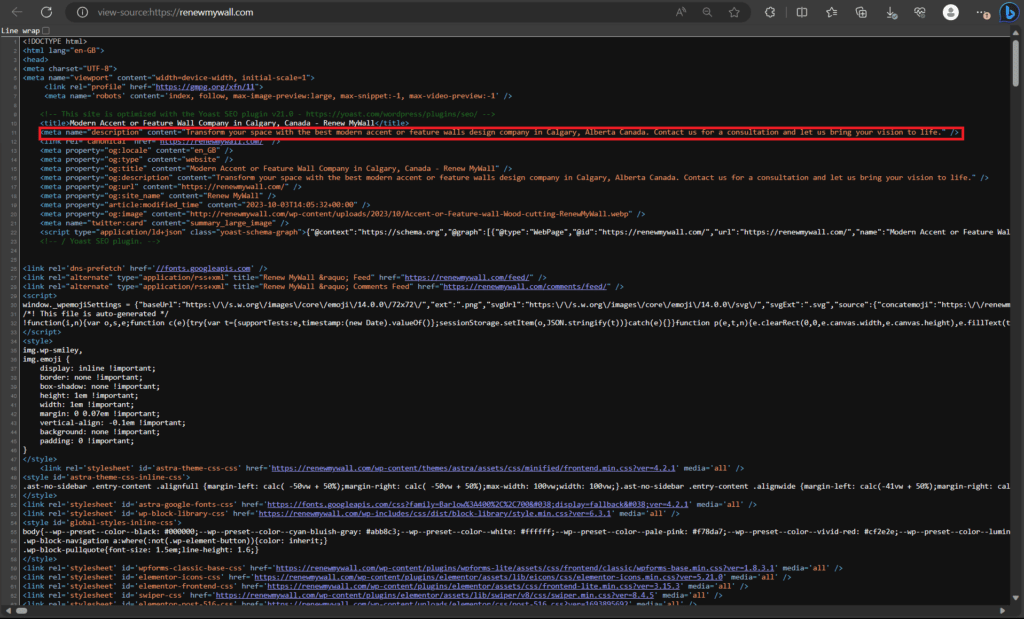
Heading Hierarchy:
Logical Structure: Organize your content with a logical heading hierarchy, starting with a single H1 (main title) and using H2, H3, and so on to indicate subtopics.
H1 for Main Topic: Use the H1 tag for your main page title, incorporating your primary keyword to signal the page’s topic to search engines.
H2 for Subtopics: Employ H2 tags for subheadings that break down the main topic into sections, helping both users and search engines understand the content’s structure.
H3 for Further Subdivisions: If needed, use H3 tags to further divide H2 sections into smaller subsections, maintaining a clear hierarchy.
Keyword Placement: Incorporate relevant keywords naturally into your headings to reinforce the content’s topic and improve SEO.
Readability: Ensure that your headings are clear and easy to read, aiding both users and search engines in comprehending your content.
Visual Appeal: Use headings to improve the visual appeal of your page, making it scannable and engaging for readers.
Mobile-Friendly: Verify that your heading hierarchy works well on mobile devices to provide a seamless user experience.
Web Content:
High-Quality Content: Create content that is valuable, informative, and engaging for your target audience.
Natural Keyword Usage: Incorporate keywords naturally throughout your content, avoiding keyword stuffing.
Engaging Introduction: Write a compelling introduction that grabs the reader’s attention and sets the tone for the content.
Clear Structure: Organize your content with headings, subheadings, and bullet points to improve readability and user experience.
Readable Formatting: Use legible fonts, appropriate font sizes, and line spacing to enhance readability.
Mobile Optimization: Ensure your content is mobile-friendly and displays well on smartphones and tablets.
User Engagement: Encourage user engagement through comments, social sharing, and calls to action (CTAs).
Proofreading: Check for spelling and grammatical errors to maintain a professional appearance.
Unique and Original: Avoid duplicate content and strive for uniqueness in your content.
Voice and Tone: Develop a consistent voice and tone that aligns with your brand and resonates with your audience.
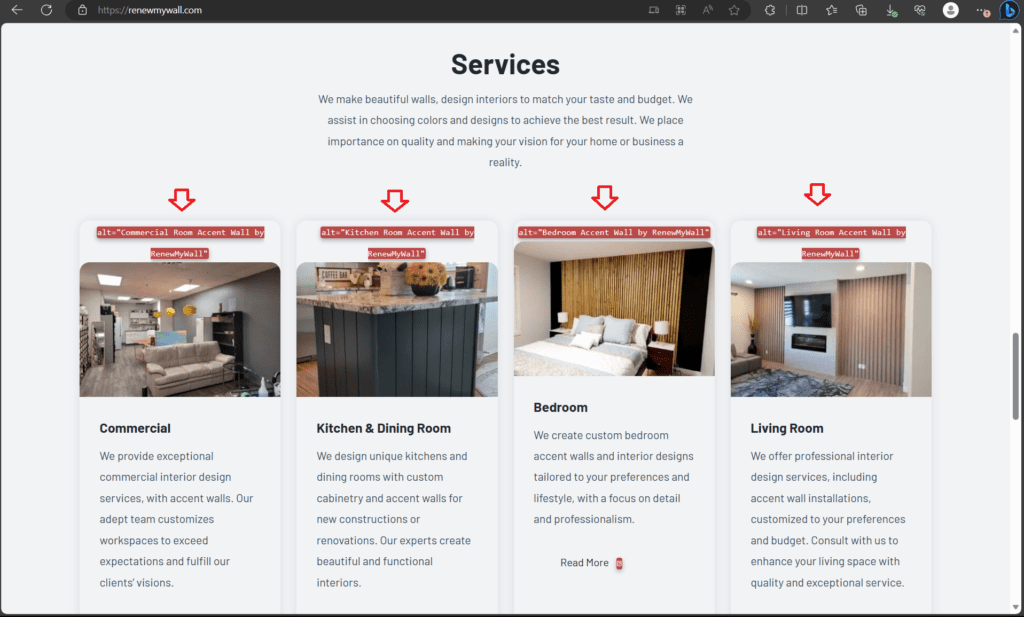
Images:
Image Relevance: Ensure that images used on your page are relevant to the content and help to convey your message effectively.
File Names: Use descriptive file names for your images, including keywords when appropriate, to provide search engines with context.
Alt Text: Always include descriptive alt text for images to improve accessibility and help search engines understand the content of the image.
Image Size: Optimize image sizes to reduce page load times, which can positively impact both user experience and SEO.
Image Formats: Choose the appropriate image format (convert to webp) to decrease the image size for fast loading.
Mobile Compatibility: Ensure that images display well on mobile devices and that they don’t negatively affect page loading times.
Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images to improve page loading speed, particularly for long-form content.
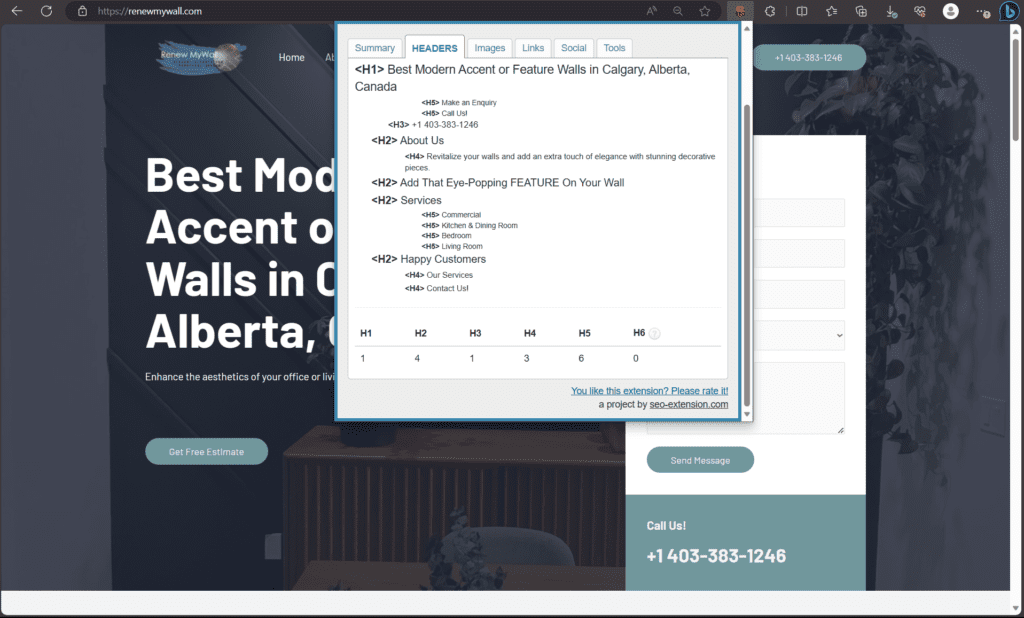
Internal Linking:
Internal linking is the practice of adding hyperlinks within your website’s content that connect to other pages on your site.
Internal links help improve website navigation, distribute link authority, and enhance user experience, which can positively impact SEO.
Relevance Matters: Link to related content that adds value to the reader’s experience and makes sense contextually.
Anchor Text: When adding links within your content, make sure the words you use as links are clear and directly related to the page you’re linking to.
Hierarchy and Structure: Organize your internal links hierarchically to reflect the structure of your website and content.
Looking for an SEO Specialist for your Business?
"Let's take it to the next level!"
If you’re a business owner, you might be wondering why it’s essential to enlist the help of an SEO Specialist to improve your website.
If SEO (Search Engine Optimization) isn’t your strong suit, you could run into some problems that might make you scratch your head. Let me help you break down these challenges you could encounter when you don’t have a good grasp of SEO.
Together, we’ll harness the magic of Search Engine Optimization strategy to ensure your brand stands out. Let’s embark on this exciting journey of growth and success!

